The most common disease of the oral cavity, after dental caries, is the inflammation of the periodontal tissue, known as periodontitis.
Periodontitis is a disease that affects the supporting tissues of the teeth, mainly the gums, bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. It is important to recognize the symptoms of periodontitis in order to start treating it in time because early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing the further advancement of periodontal diseases.
The initial inflammation of the gums is called gingivitis and it is the mildest form of periodontal disease. It is caused by soft and hard deposits (tartar) on the teeth that contain pathogenic bacteria. Inflamed gums are swollen, painful to the touch, and bleed when brushing.
If gingivitis is not treated in time, it can lead to periodontitis.
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammation of the gums and structures surrounding the tooth.
It causes destruction of the bone and the fibers that connect the bone and the tooth, which leads to the formation of periodontal pockets that deepen over time and ultimately lead to loosening and loss of teeth. It is important to note that advanced periodontitis can increase the risk of other systemic conditions in the body by allowing bacteria to enter the bloodstream.
Periodontal treatment consists of three phases.
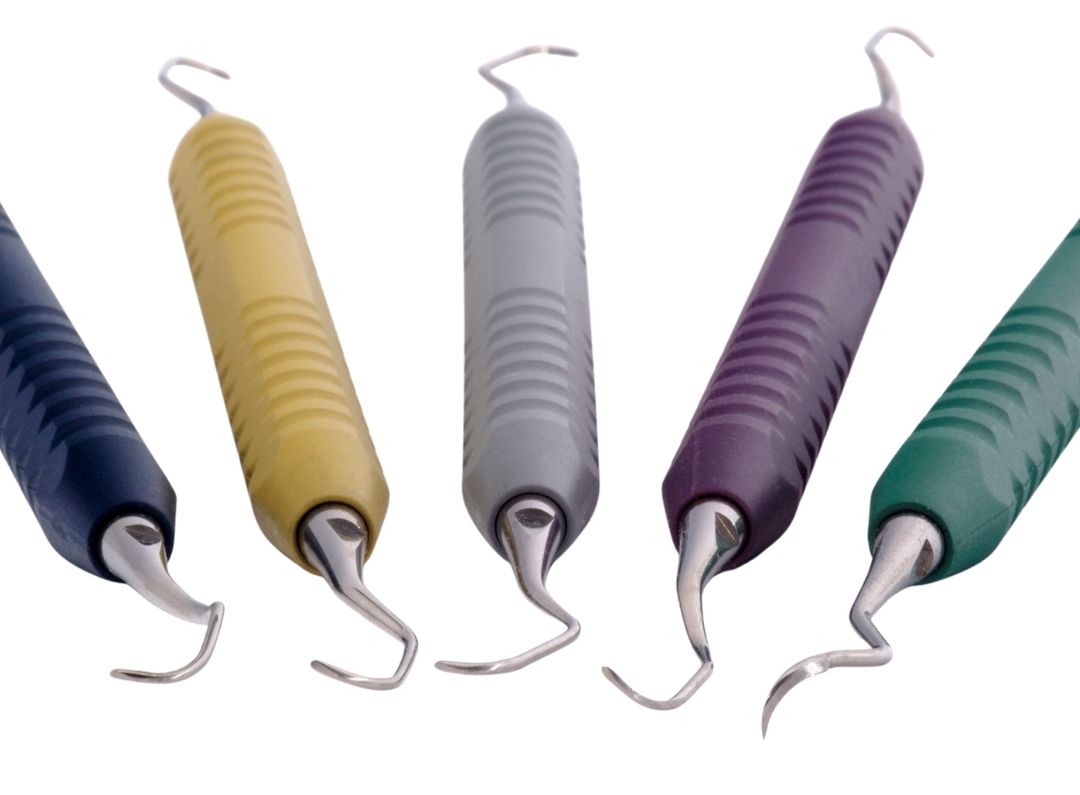
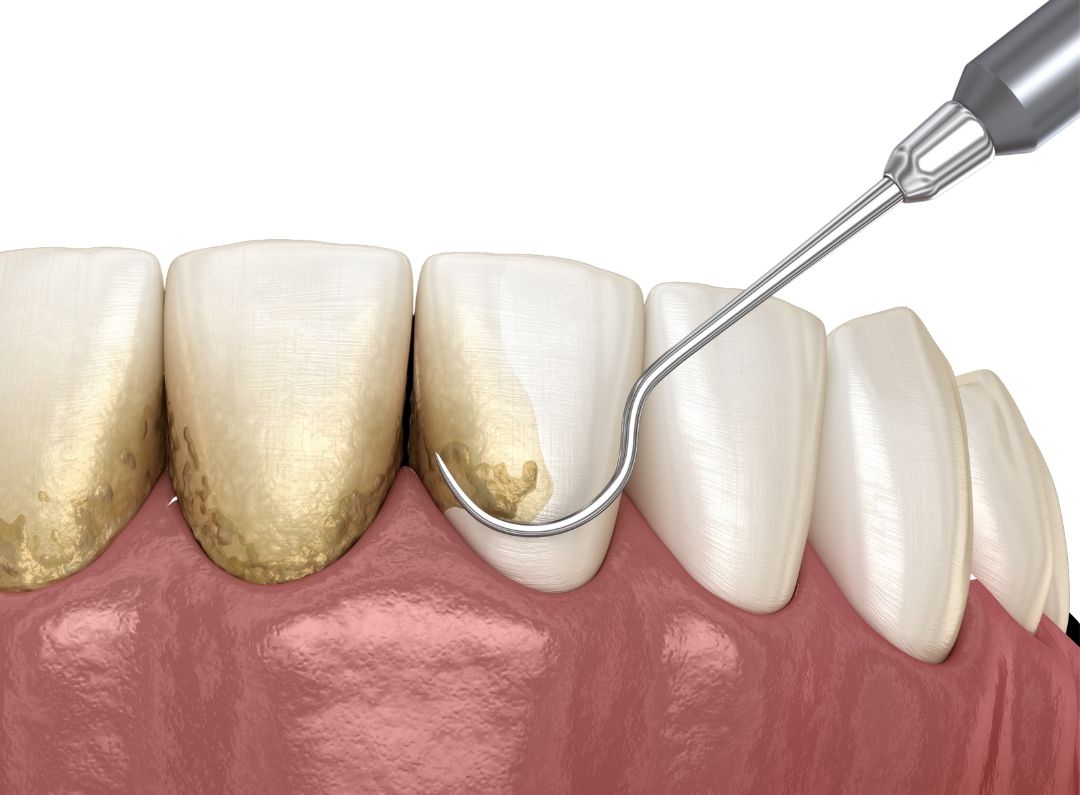
The first phase consists of measuring the depth of the periodontal pockets and other parameters, followed by the initial treatment, which includes scraping and polishing soft and hard deposits from dental roots using manual and ultrasonic instruments.
The first phase of treatment is also known as dental curettage or deep cleaning. The initial treatment is carried out under local anesthesia, ensuring the painlessness of the procedure. Antibiotic therapy depends on the individual case and is not prescribed for every patient.
When it comes to the second phase of the treatment, our patients play a big role. It requires great commitment, and regular and detailed oral hygiene according to the instructions of our doctors.
It includes regular check-ups, as well as regular removal of plaque on the teeth in order to heal the gums and eliminate bacteria. The first phase often needs to be repeated after a trial number of months if we notice that healing is not completely successful.
Gingivitis

Oral hygiene – regular examinations
Surgery if necessary